wait()函数定义
1
2
3
4
| #include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
pid_t wait(int *status)
// 参数status用来保存被收集进程退出时的一些状态,它是一个指向int类型的指针。但如果我们对这个子进程是如何死掉的毫不在意,只想把这个僵尸进程消灭掉,(事实上绝大多数情况下,我们都会这样想),我们就可以设定这个参数为NULL,如pid=wait(NULL),返回给pid的值就是子进程的id
|
WIFEXITED(status)/WEXITSTATUS(status)
当子进程正常结束时,WIFEXITED(status) 返回非0值;当子进程异常结束时,WIFEXITED(status) 返回0值
WEXITSTATUS(status)在WIFEXITED(status)为非0时可以用来获取exit()中的参数即返回给父进程的值,如果子进程调用exit(5)退出,WEXITSTATUS(status)就会返回5;如果进程不是正常退出的,也就是说,WIFEXITED返回0
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
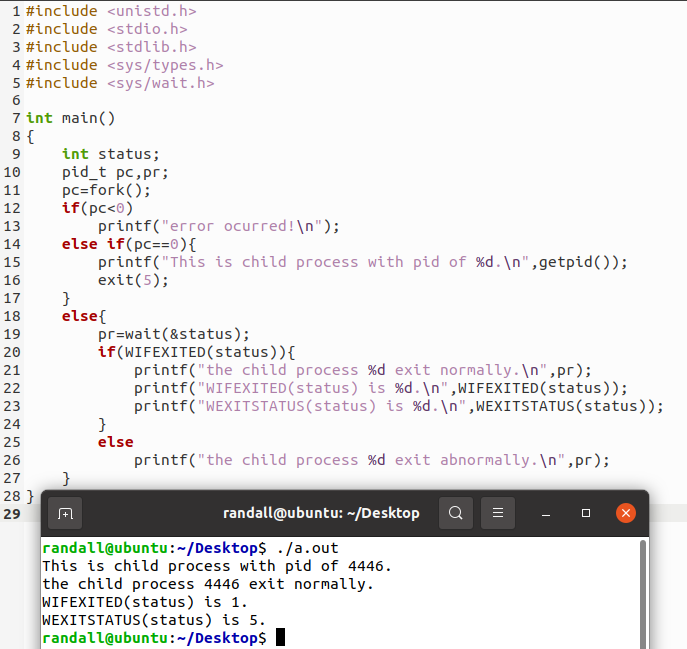
| #include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
int main()
{
int status;
pid_t pc,pr;
pc=fork();
if(pc<0)
printf("error ocurred!\n");
else if(pc==0){
printf("This is child process with pid of %d.\n",getpid());
exit(5);
}
else{
pr=wait(&status);
if(WIFEXITED(status)){
printf("the child process %d exit normally.\n",pr);
printf("WIFEXITED(status) is %d.\n",WIFEXITED(status));
printf("WEXITSTATUS(status) is %d.\n",WEXITSTATUS(status));
}
else
printf("the child process %d exit abnormally.\n",pr);
}
}
|